
He wanted to know more about the physical properties of these particles, like their mass. Thomson had concluded that the cathode rays themselves consisted of negatively charged particles. This showed that the charge carried by the cathode rays was negative.

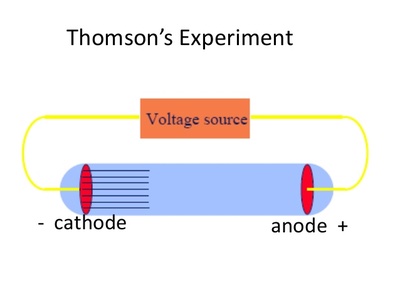
When the charged metal plates were introduced he found that the cathode rays bent toward the positive plate and away from the negative plate. Instead of an electrometer at one end of the CRT he now had a fluorescent coating that would glow where the cathode ray hit it. He put a negatively charged metal plate on one side of the cathode rays let out past the anode, and a positively charged metal plate on the other side. To do this he would use an electric field. Thomson set out to determine if the charge carried by the cathode rays was negative or positive. From this he deduced that the electric charge and the cathode rays must be combined together and not separate entities.Next, J.J. When he did this, he discovered that the electrometers stopped measuring electric charge. Thomson used a magnet to bend the cathode rays away from the electrometers. When the cathode rays hit the electrometer, it measured an electric charge.The first experiment was done in order to see if the charge was separate from the cathode rays. This was done by putting an electrometer at the opposite end from the cathode and anode. Before Thomson’s experiments, it had already been discovered that the cathode rays deposit an electric charge. Instead, it was a result that was slowly built towards over the course of three different experiments. Thomson’s discovery of electrons didn’t happen all at once. Instead, what flowed off the cathode toward the anode were called ‘cathode rays.’ Hence the name cathode ray tube. So, no one was calling it an electron beam. Thomson to see where the electron beam was hitting.Of course, before his experiment, we didn’t know electrons existed. On the opposite side of the tube is a coating that glows when struck by the electrons. Electrons, which have a negative charge, flow off the cathode and are attracted towards the anode.Ī small hole in the anode allows some electrons to pass through it, creating a beam of electrons. The cathode is a negatively-charged conductor, and the anode is a positively-charged conductor. On one side of the inside of the tube there’s a cathode and an anode. The CRT consists of several elements starting with a tube that’s vacuum sealed to keep air out of it. Thomson would’ve used, as seen in the diagram below.

Thomson used the cathode ray tube to discover the electron, we need to know how a cathode ray tube works. Thomson to discover the existence of electrons in 1897.īefore we see how J.J. It was cathode ray tubes that allowed the English physicist J.J. However, cathode ray tubes have been used for more than entertainment. The CRT in a television is used to display images on your screen. You might have used a cathode ray tube even if you’ve never even heard of it until reading this lesson.īefore LCD and Plasma TVs became commonplace, most people used bulkier cathode ray tube (CRT) televisions. * All Partners were chosen among 50+ writing services by our Customer Satisfaction TeamĬathode Ray Tubes in Your Home Portrait of J.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
